
Must-Have Technical Skills of a Website Project Manager
Managing a website project can be demanding, especially when balancing it with running a business. This is why many organizations employ web project managers to help plan, design, develop, and manage their sites or applications, resulting in seamless operations.
Based on Upwork’s findings, 65% of projects fail, highlighting the crucial role of project managers in success. Many organizations hire them to coordinate teams to ensure that final products are aligned with established goals.
Project managers find solutions to meet project goals within deadlines and ensure timely delivery.

Source: Exploding Topics.
With the leadership of a professional project manager, development professionals can efficiently and effectively build, develop, and manage sites and apps.
Web Project Managers vs Dedicated Project Managers: The Difference
Project managers for web and dedicated projects have similar skill sets but focus on different areas:
Website project managers oversee the web development project lifecycle. They coordinate teams to build or maintain websites on time and meet business goals.
For instance, project managers usually define the project’s technical scope using web-centric methodologies such as Agile.
To meet the unique demands of web-based projects, these professionals possess an in-depth understanding of:
- Web technologies;
- Coding languages;
- Development tools;
- Communication and coordination;
- Troubleshooting and problem-solving, and
- Project management software.
As such, web project managers streamline communication and effectively manage complex projects.
Meanwhile, dedicated project managers work with a team on a broader spectrum of projects such as for IT or product development.
A dedicated project manager will often tailor their strategies based on the industry and specific project requirements. As such, they demonstrate flexibility in adapting to diverse scopes, budgets, and stakeholder needs.
In summary, while these two types of project managers share core skills, their technical knowledge differs according to their respective industries and projects.
8 Must-Have Technical Skills of a Website Project Manager
A seasoned project manager drives the web development process, equipped with the following skills:
Knowledge of IT Infrastructure and Architecture
Experienced project managers are knowledgeable of their clients’ IT infrastructure and architecture, including:
- Composite hardware;
- Software;
- Network resources, and
- Services.
These elements are necessary for the existence, operation, and management of a company’s IT environment.
Moreover, project managers have a background on the role of IT architects in designing hardware, software, network, solutions, and services. These define business models, specifications, implementation road maps, and other guidelines.
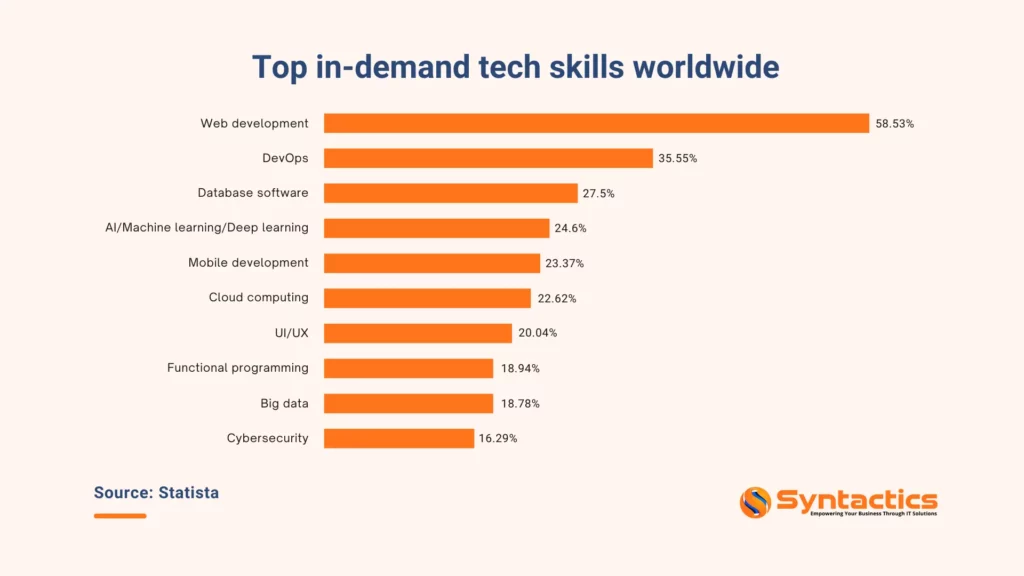
Source: Statista.
Project Planning and Methodologies
Seasoned project managers possess the planning and scheduling skills necessary to keep development on track. They outline tasks, establish project timelines, and allocate resources efficiently.
In addition, they’re well-versed in various project management methodologies such as Waterfall, Agile, and Hybrid.
Technical Documentation
Thorough project documentation enhances transparency and streamlines operations. It’s crucial for project managers to create detailed documentation throughout the development process, often including the following:
- Project planning;
- Resource allocation;
- Gantt chart;
- Risk and mitigation, etc.
Documentation reports enable businesses to analyze past web projects, making it easier to analyze the results and make informed decisions, especially for future projects.
An effective website project manager supervises the team to ensure timely project delivery. They utilize spreadsheet tools such as MS Excel and Google Sheets to outline the overall plan, timeline, and each team member’s respective tasks.
Communication and Client Management
Communication is a vital soft skill for web project management. Project managers excel in effectively communicating with the rest of the team.
Additionally, project managers are the bridge between clients and development teams. They provide regular updates, facilitate collaboration, and hold discussions to keep everyone informed about project progress.

Source: FitSmallBusiness.
Seasoned project managers are adept in technical and non-technical language, enabling them to effectively address project-related issues and concerns among stakeholders.
As part of their client management skills, a project manager is open to ideas and suggestions. Most importantly, they’re capable of getting along with all sorts of individuals, guaranteeing smooth project implementations for success.
Risk Management and Adaptability
Project managers possess strong risk management skills, enabling them to swiftly address potential issues that could hinder project progress.
They can also communicate changes to stakeholders — whether related to scope, schedules, or resources — to all involved parties.
They’re adaptable professionals in a dynamic, ever-evolving industry, making them an ideal choice to lead your dedicated development team.
Budget and Finance Management
Finances are essential to project success. As leaders of development teams, project managers are adept at financial management, including budgeting and cost control.
To prevent budget overruns, project managers compare actual expenses with projected costs.
Alongside forecasting costs and allocating resources, they regularly provide financial reports to keep all parties involved informed about finances.
At the start of a project, these professionals estimate the financial resources needed to achieve a client’s objectives.
This approach allows them to maximize expenses to achieve optimal results in the shortest time possible.
Quality Assurance (QA) Expertise
A project manager with Quality Assurance expertise is invaluable in crafting reliable, high-performing web projects.
Many web development teams include QA testers who perform rigorous tests on projects, meticulously examining functionality, visuals, usability, and performance.
However, project managers with QA skills are vital for identifying issues early and preventing delays for web development success.
As a result, they enhance project usability and ensure the delivery of top-quality end products.
Design and Analysis Tools
A project manager utilizes advanced design and analysis tools or programs to plan, implement, and manage every team member’s tasks, workload, and deliverables.
Among the top picks for project management tools include:
- Project collaboration tools (e.g., Basecamp, Asana, Slack);
- Flowcharts;
- Diagrams and wireframes (e.g., Moqups, Mockingbird, Lucidchart), and
- Mockups and prototypes (e.g., Invision, Adobe XD, MS Paint).
Conclusion
Managing a variety of web projects can be overwhelming in today’s competitive digital landscape.
Fortunately, a project manager’s skills can help deliver high-quality websites or web apps that meet accepted standards and client expectations.
These professionals possess various technical skills that can bridge the gap between a client’s vision and technical execution. They streamline and oversee project development, ensuring that everything stays on schedule.
A project manager can assist you in planning, building, and managing your web projects for success.
This article was updated on November 13, 2024.
Frequently Asked Questions About Website Project Managers
What is web project management?
Website project management involves planning, implementing, and overseeing development to completion. Project managers facilitate the development process, managing resources, and ensuring timely product delivery.
What does a web project manager do?
A web project manager coordinates teams, sets project timelines, manages budgets, and ensures project milestones are met throughout the project development lifecycle.
What technical skills should a website project manager have?
Here are the key skills a web project manager should have:
- IT infrastructure and architecture
- Project planning and methodologies
- Technical documentation
- Communication and client management
- Risk management and adaptability
- Budget and finance management
- Quality Assurance (QA) expertise
- Design and analysis tools

















Comment 0